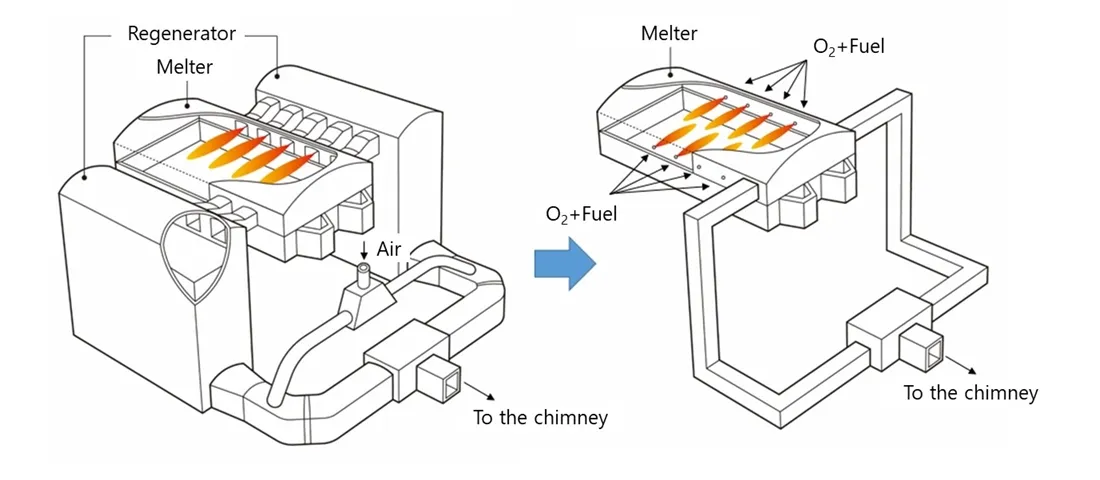
Large glass-melting furnaces for glass bottles in Japan currently use air combustion, but air contains about 80% nitrogen, which becomes exhaust gas without contributing to heat transfer in the glass-melting process. Combustion with air is therefore an inefficient use of energy and a significant obstacle to reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
By introducing an oxygen combustion system, which has high efficiency of heat transfer to glass due to the absence of nitrogen, while maintaining the current production capacity is expected to reduce GHG emissions by approximately 20% for each glass-melting furnace. Furthermore, the use of bricks for heat storage in the exhaust gas of air combustion furnaces will no longer be necessary, enabling the construction of environmentally friendly, resource-conserving, and waste-reducing melting furnaces. However, new equipment for supplying oxygen will be necessary, with its associated operating costs. Nevertheless, we made this decision with the understanding of all our customers in order to take another step forward in meeting our corporate obligation to reduce GHG emissions.
Glass bottles are environmentally friendly containers that not only protect their contents but also comply with the 3Rs (reduce, reuse, recycle). With the introduction of oxygen combustion, TOYO GLASS is further developing and applying technologies to reduce GHG emissions and lower the environmental impact of glass bottle manufacturing.
For inquiries about this press release, please contact
Nakanori / Kakimoto
Corporate Communication Group
Sustainability Department
Toyo Seikan Group Holdings, Ltd.
(Email) tskg_contact@tskg-hd.com